Published on September 19, 2024
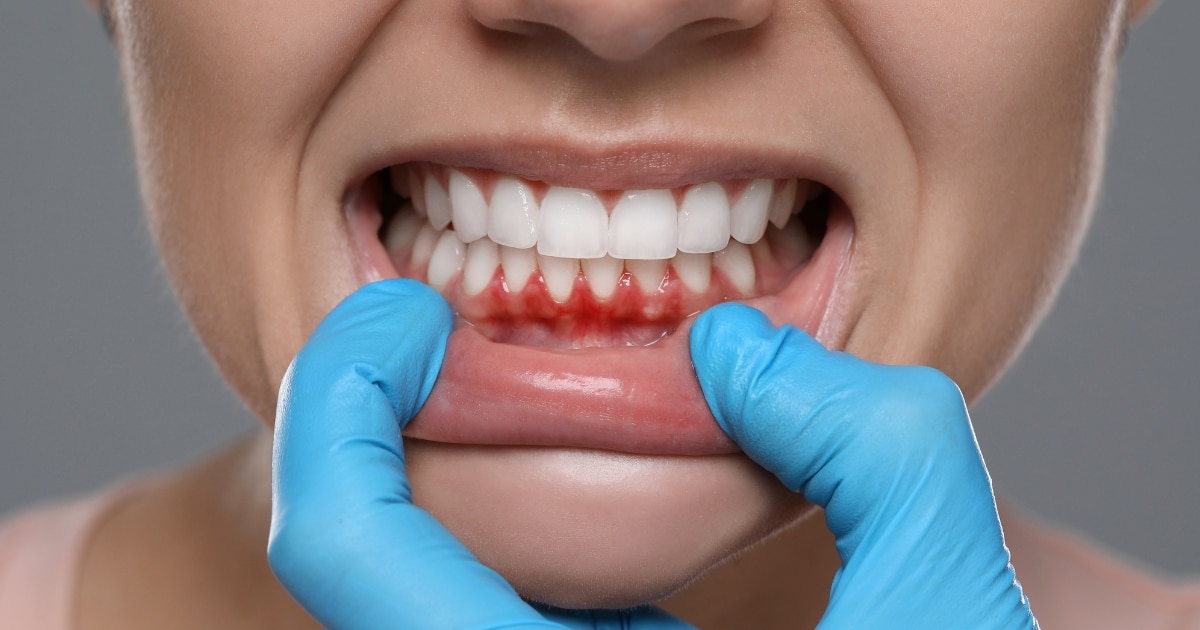
Bruised gums are more common than you might think. You may notice your gums feeling tender or see a darker spot after brushing, but most people don’t give it a second thought.
However, bruised gums can be a sign that something’s not quite right in your oral health routine. Ignoring it could lead to bigger issues down the road, and nobody wants that.
In this blog, we’ll explore the causes behind bruised gums and how you can treat them effectively. Whether it’s from brushing too hard or something more serious like gum disease, there are steps you can take to heal and prevent future bruising.
Let’s dive into what’s causing your gum pain and how you can fix it before it becomes a bigger problem.
Common Causes of Bruised Gums
Bruised gums can result from several everyday habits or health conditions. Understanding these causes helps you take proactive measures to protect your oral health. Here are some common culprits behind bruised gums:
- Dental Trauma: An injury from a hard object, like a toothbrush or food, can bruise your gums. This often occurs during activities like sports or accidents.
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a stiff-bristled toothbrush can damage gum tissue, leading to bruising. It’s essential to use gentle strokes and the right tools.
- Gum Disease: Conditions like gingivitis or periodontitis can cause inflammation and bruising. Bacteria infect the gums, leading to swelling and tenderness.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to bruising.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as blood disorders or vitamin deficiencies, can increase your risk for bruised gums. Always consult a healthcare provider if you notice unexplained bruising.
Signs and Symptoms to Look For
Recognizing the signs of bruised gums is essential for effective treatment. Being aware of these symptoms helps you take prompt action and avoid potential complications. Here’s what to look for:
- Discoloration: Bruised gums may appear darker than usual. Look for shades of red, purple, or blue that indicate bruising.
- Swelling: A swollen gum line can accompany bruising. This may cause discomfort or difficulty when eating or brushing.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity or tenderness in the affected area often signals an issue. You may feel pain when brushing or consuming hot and cold foods.
- Bleeding: Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing may indicate underlying problems. If bruising appears with frequent bleeding, take it seriously.
- Persistent Symptoms: If bruising continues for an extended period without improvement, it may signify a more significant issue requiring professional attention.
How to Treat Bruised Gums at Home?
- Gentle Brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently to avoid further irritation. Aim for a circular motion rather than aggressive scrubbing.
- Saltwater Rinses: Mix one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and use it as a mouth rinse. This can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and swelling. Always follow the dosage instructions.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress on the outside of your mouth can reduce swelling and numb pain. Use it for about 10–15 minutes at a time.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated and eat a soft diet. Avoid spicy, hot, or acidic foods that could further irritate your gums.
When to See a Dentist for Bruised Gums?
Sometimes, bruised gums require professional attention. Knowing when to seek help can prevent serious complications. Here are situations that warrant a visit to your dentist:
- Persistent Bleeding: If your gums bleed frequently or excessively, it may indicate a deeper issue. Chronic bleeding should never be ignored.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain or discomfort that doesn’t subside with over-the-counter medications is a sign to see your dentist. You shouldn’t have to live with pain.
- Recurring Bruises: If you notice bruising reoccurring without a clear cause, it’s essential to investigate further. This could point to underlying health problems.
- Signs of Infection: If you see pus, experience swelling, or have a fever along with your bruised gums, these are signs of infection that need immediate attention.
- Changes in Gum Health: Any sudden changes in your gum condition or overall oral health should prompt a visit. This includes increased sensitivity or noticeable shifts in gum color.
Bruised gums may seem like a minor issue, but they can signal deeper health concerns. By understanding the causes and symptoms, you empower yourself to take charge of your oral health. Remember to treat minor bruises at home, but don’t hesitate to seek professional advice when necessary. Your gums deserve the best care possible! Stay proactive and keep your smile shining bright. Have questions or concerns? Your dentist is just a call away!
