Published on June 27, 2024
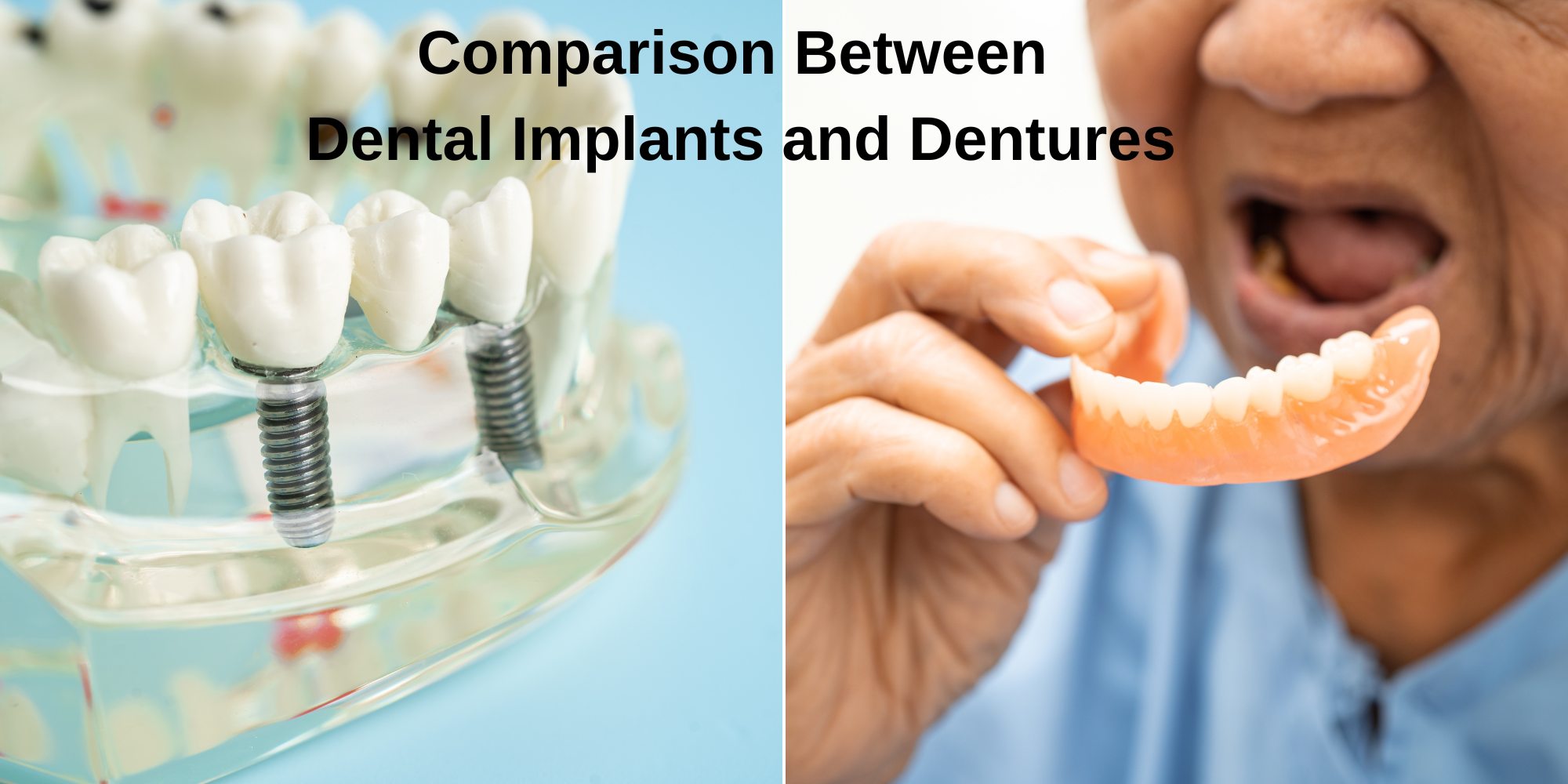
In the realm of dental restoration, the choice between dental implants and dentures can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Both options offer unique benefits and considerations, making it crucial to understand their differences before making a decision. Dental implants, renowned for their stability and resemblance to natural teeth, involve surgically placing titanium posts into the jawbone.
This process allows them to integrate securely, offering robust support for crowns or bridges. On the other hand, dentures, available in complete or partial forms, provide a removable alternative suitable for varying degrees of tooth loss.
The decision between dental implants and dentures hinges on factors such as oral health, lifestyle, and budget. Understanding these aspects empowers individuals to choose the option that aligns best with their needs.
This blog delves into the comparative aspects of durability, cost, aesthetics, maintenance, and more, aiming to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this pivotal dental decision confidently. Whether you’re exploring long-term solutions or seeking immediate restoration, let’s explore how each option can enhance your smile and overall dental health.
Definition and Components of Dental Implants
- Dental implants are prosthetic devices designed to replace missing teeth permanently.
- Consist of three main components: the implant fixture, abutment, and prosthetic crown.
- The implant fixture is typically made of titanium, surgically placed into the jawbone.
- Abutment connects the implant fixture to the prosthetic crown, providing support and stability.
Placement and Integration Process
- Initial surgical procedure involves placing the implant fixture into the jawbone.
- Over time, the bone tissue grows around and integrates with the implant fixture, a process called osseointegration.
- Abutment is attached to the implant fixture after osseointegration, allowing for attachment of the prosthetic crown.
- Prosthetic crown is custom-made to match the natural teeth in shape, size, and color, ensuring a natural appearance.
Types of Dentures
Complete Dentures
- Complete dentures replace all teeth in the upper or lower jaw.
- They are typically made of acrylic material and rest directly on the gums.
- Upper complete dentures cover the roof of the mouth (palate) for suction.
- Lower complete dentures are shaped like a horseshoe to accommodate the tongue.
Partial Dentures
- Partial dentures replace one or more missing teeth and are attached to existing teeth.
- They can be made of acrylic or metal framework with acrylic teeth.
- Metal partial dentures are more durable and provide better support.
- Acrylic partial dentures are less expensive but may need more frequent adjustments.
Comparison of Durability and Longevity
Lifespan of Dental Implants vs. Dentures
Dental Implants:
- Longevity: Dental implants are designed to be a long-term solution, often lasting a lifetime with proper care.
- Durability: They are made of biocompatible titanium and integrate with the jawbone, providing stability and strength similar to natural teeth.
- Maintenance: Minimal maintenance beyond regular oral hygiene and periodic check-ups.
Dentures:
- Lifespan: Typically last around 5-10 years, but may need replacement due to wear or changes in the jawbone.
- Durability: Made of acrylic or a combination of materials, they are more prone to wear and tear compared to implants.
- Maintenance: Require daily cleaning and occasional adjustments or relining for optimal fit and function.
Factors influencing durability:
- Bone Density: Implant success depends on sufficient jawbone density.
- Oral Hygiene: Good oral care prolongs the lifespan of both implants and dentures.
- Medical Conditions: Health issues like diabetes can affect the healing and longevity of implants.
Aesthetics and Natural Feel
Appearance and Natural Look of Dental Implants:
- Natural Integration: Dental implants are designed to closely mimic natural teeth, both in appearance and function.
- Customization: They are customized to match the color, shape, and size of adjacent teeth, ensuring a seamless blend.
- Gum Line: Implants emerge naturally from the gum line, enhancing facial aesthetics and smile symmetry.
Discussing the Aesthetics and Fit of Modern Dentures:
- Improved Materials: Modern dentures use advanced materials that closely resemble natural teeth in color and texture.
- Customization: Dentures are individually crafted to fit the contours of the gums, enhancing comfort and natural appearance.
- Stability: Innovative designs like implant-supported dentures provide better stability and prevent slippage, improving confidence.
Maintenance and Care
Daily Care Routines for Dental Implants:
- Brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste to clean implant crowns and surrounding teeth.
- Flossing: Regular flossing or interdental brushes help remove plaque and debris from around the implant.
- Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and maintain oral hygiene.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule routine check-ups with your dentist for professional cleaning and to monitor implant health.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips for Dentures:
- Brushing: Brush dentures daily with a denture brush and non-abrasive denture cleaner to remove food particles and plaque.
- Soaking: Soak dentures overnight in a denture cleaning solution or water to keep them moist and clean.
- Handling: Handle dentures carefully to avoid damage; rinse them after meals and before placing them back in your mouth.
- Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist for adjustments and inspections ensure proper fit and function of dentures.
Bone Health and Jawbone Preservation
Impact of Dental Implants on Jawbone Stimulation:
- Osseointegration: Dental implants stimulate the jawbone similarly to natural tooth roots, preventing bone loss.
- Preservation of Bone Density: Implants maintain jawbone density by transmitting chewing forces, which stimulate bone growth.
- Long-term Stability: Properly integrated implants can preserve facial structure and prevent deterioration over time.
How Dentures Affect Jawbone Health Over Time?
- Bone Resorption: Dentures rest on the gum ridge without stimulating the jawbone, leading to bone loss over time.
- Changes in Fit: As bone resorption occurs, dentures may become loose, requiring adjustments or relining.
- Impact on Facial Appearance: Reduced jawbone support can alter facial contours and cause facial sagging.
Suitability for Different Dental Conditions
Factors Determining the Suitability of Dental Implants:
- Bone Density: Sufficient jawbone density is crucial for successful implant placement and integration.
- Overall Health: Patients should be in good health to undergo surgery and healing associated with implants.
- Oral Health: Healthy gums and the absence of periodontal disease are essential for implant success.
- Cosmetic Considerations: Implants are ideal for individuals seeking a natural-looking and permanent tooth replacement option.
- Chewing Ability: Implants offer superior chewing function compared to dentures due to their stability.
When Dentures Might Be a Better Option:
- Bone Loss: Individuals with significant jawbone resorption may not have enough bone for implant placement.
- Cost Considerations: Dentures are typically more affordable initially than dental implants.
- Health Constraints: Some patients may have medical conditions that make surgery for implants risky.
- Temporary Solution: Dentures can be used as a temporary measure while waiting for bone grafting or implant healing.
- Adjustability: Dentures allow for easier adjustments and modifications compared to implants.
Patient Experience and Comfort
Comfort Levels with Dental Implants vs. Dentures:
- Implants: Initially, there may be discomfort during the healing process post-surgery, but once integrated, implants feel natural and secure.
- Dentures: Some discomfort is common initially as the mouth adjusts to the prosthesis. Dentures can occasionally cause irritation or sore spots.
Adjusting to and Living with Each Type of Dental Restoration:
- Implants: Provide stability and mimic natural teeth, enhancing confidence in chewing and speaking. Little maintenance beyond regular oral hygiene is needed.
- Dentures: Require adaptation to eating and speaking due to their removable nature. Regular adjustments may be necessary as the jawbone changes over time.
- Psychological Impact: Implants often boost self-esteem due to their permanence, while dentures may initially impact self-confidence until adjusted to.
Cost Considerations
Upfront Costs of Dental Implants:
Dental implants typically have higher initial costs due to surgical procedures, including placement of the implant post and crown.
Long-Term Financial Implications:
- Durability and Lifespan: Implants are durable and can last a lifetime with proper care, potentially reducing long-term costs compared to dentures.
- Maintenance: Minimal maintenance is required beyond routine dental care, which can lead to lower ongoing costs.
Comparing Costs of Different Types of Dentures:
- Complete Dentures: Generally more affordable upfront, but ongoing adjustments and replacements may increase long-term costs.
- Partial Dentures: Costs vary depending on materials used and the number of teeth replaced, with some requiring periodic adjustments.
Choosing between dental implants and dentures depends on various factors such as oral health, lifestyle, and financial considerations. While implants offer durability and jawbone preservation, dentures provide affordability and adaptability. Understanding these differences allows individuals to make informed decisions aligned with their needs and preferences.
