Published on June 9, 2024
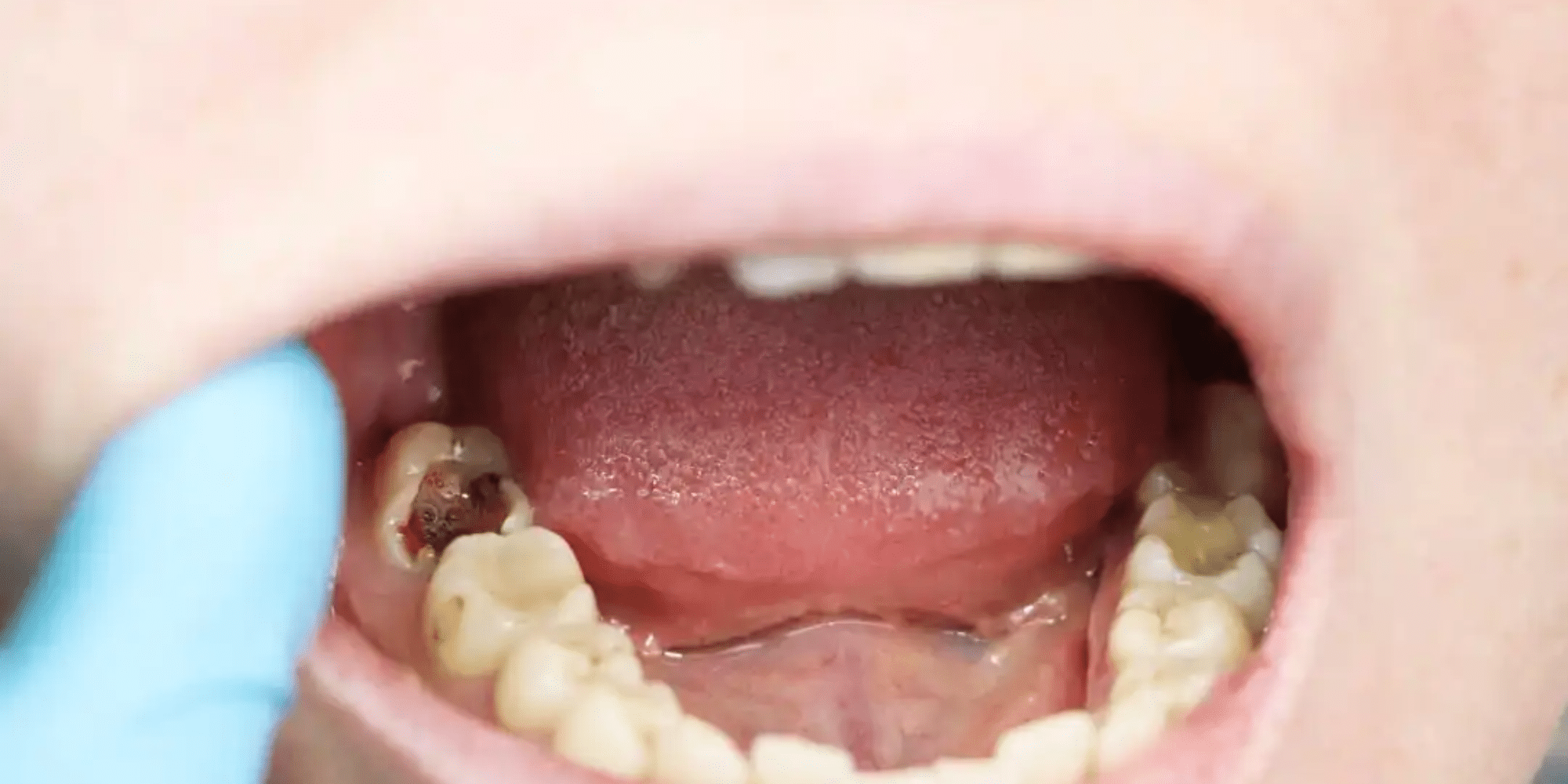
Maintaining good oral health is essential for overall well-being, and understanding the signs of a severe cavity plays a crucial role in proactive dental care. A cavity, or tooth decay, is a common dental issue caused by bacteria that erode tooth enamel over time. Recognizing when a cavity becomes serious is vital to prevent complications that can affect both dental and systemic health.
When a cavity progresses beyond the initial stages, it can lead to significant dental problems. Early signs such as sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods may escalate to persistent toothaches and visible holes or pits in the teeth. These symptoms indicate that the decay has reached an advanced stage, potentially affecting deeper layers of the tooth.
As such, knowing the indicators of a severe cavity empowers individuals to seek timely treatment from a dentist, thereby safeguarding their oral health and avoiding more extensive interventions later on. Understanding these signs enables proactive management of dental health, promoting a healthier smile and overall quality of life.
Understanding Dental Cavities
Tooth decay, commonly known as dental cavities, results from a combination of factors and progresses over time due to specific mechanisms:
Definition of Tooth Decay:
- Tooth decay occurs when acids produced by bacteria in plaque erode the enamel, the outer layer of the tooth.
- Without intervention, decay can penetrate deeper layers, leading to structural damage and potential tooth loss.
Causes of Tooth Decay:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, promoting decay.
- Dietary Factors: Sugary and starchy foods feed bacteria that produce acids, contributing to enamel erosion.
- Bacterial Presence: Streptococcus mutans and other bacteria in the mouth metabolize sugars into acids that attack tooth enamel.
Development of Cavities Over Time:
- Initial Stage: Plaque buildup begins to demineralize enamel, creating small pits or areas of discoloration.
- Progression: Acid erosion deepens, forming larger cavities that may cause sensitivity and pain.
- Advanced Stages: Decay can extend to the dentin and pulp, leading to infections, abscesses, and severe tooth damage.
Signs and Symptoms of a Bad Cavity
Identifying the signs and symptoms of an advanced cavity is crucial for timely intervention and preserving dental health.
Early Warning Signs:
- Tooth Sensitivity:
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks may indicate enamel erosion and early decay.
- Discomfort that lingers after exposure to temperature changes warrants attention.
- Mild Pain or Discomfort:
- Persistent, dull pain or occasional twinges when chewing could signal decay reaching deeper layers of the tooth.
- Pain that comes and goes intermittently may indicate early nerve involvement.
Advanced Symptoms:
- Visible Holes or Pits:
- Visible cavities or holes in the teeth are clear indicators of advanced decay.
- These cavities may appear as dark spots or pits on the surface of the affected tooth.
- Tooth Discoloration:
- Discoloration, ranging from white spots to dark brown or black areas on the tooth surface, signals significant enamel breakdown.
- Discoloration may be localized or spread across the affected tooth.
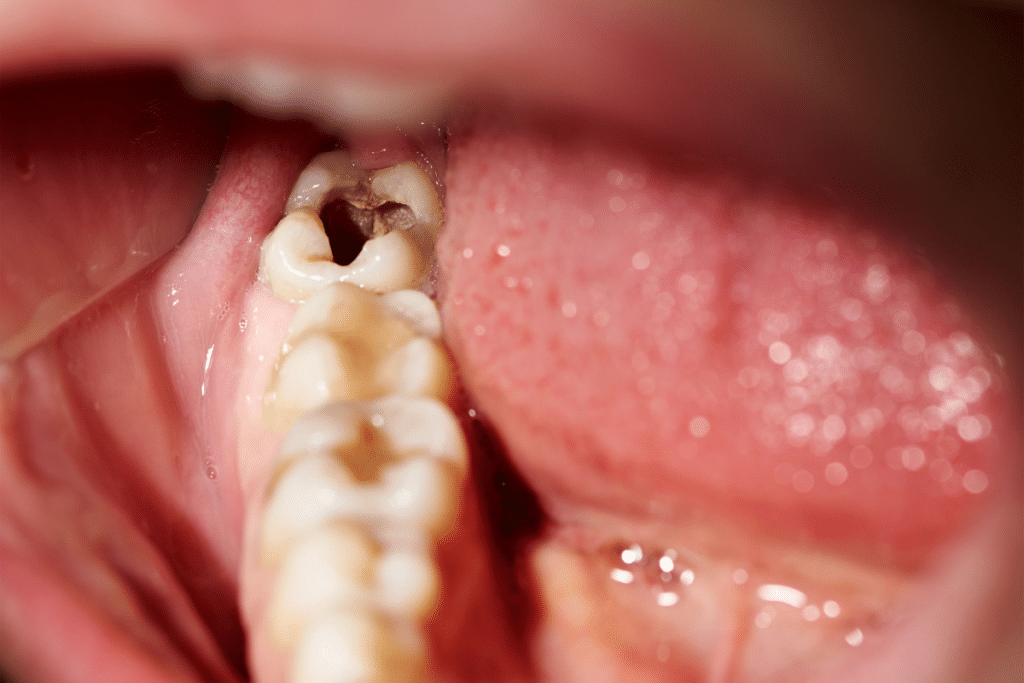
Complications of Untreated Cavities
Untreated cavities can lead to various complications that affect both oral health and overall well-being:
Potential Risks to Oral Health:
- Infection:
- Bacteria from decay can penetrate deep into the tooth, leading to a bacterial infection.
- Infection may cause severe pain, swelling, and even the formation of an abscess at the root of the tooth.
- Abscess Formation:
- An abscess is a pus-filled pocket that forms at the root of a tooth due to untreated decay or infection.
- It can cause intense pain and swelling of the face or jaw and may lead to systemic infections if left untreated.
Impact on Overall Health:
- Systemic Complications:
- Untreated oral infections can spread beyond the mouth, potentially affecting other parts of the body.
- Research suggests links between oral infections and systemic conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Effective diagnosis of cavities involves thorough assessment and examination methods to determine the extent of decay:
Dental Examination:
- Visual Inspection: Dentists visually examine teeth for signs of decay, such as discoloration, pits, or visible holes.
- X-rays (Radiographs): X-rays provide detailed images of tooth structures, revealing decay between teeth or under existing fillings.
Severity Assessment:
- Dentists assess the severity of decay based on visual findings and X-ray results.
- They classify cavities by size and depth to determine appropriate treatment options, from dental fillings to more extensive procedures like root canals.
Treatment Options for Severe Cavities
When cavities progress to a severe stage, several treatment options are available depending on the extent of damage and the condition of the affected tooth:
Dental Fillings: Materials and Effectiveness
- Materials: Common materials used for fillings include amalgam (silver), composite resin (tooth-colored), and porcelain.
- Effectiveness: Fillings restore the tooth’s structure and function by filling in the cavity, preventing further decay, and strengthening the tooth.
Root Canal Therapy: When Is It Necessary?
- Indications: Required when decay reaches the tooth pulp, causing infection or inflammation.
- Procedure: Involves removing infected pulp, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection.
Tooth Extraction: Last Resort
- Reasons: Reserved for cases where the tooth cannot be saved due to extensive decay, trauma, or infection.
- Considerations: Extraction is followed by options like dental implants or bridges to restore chewing function and prevent neighboring teeth from shifting.
When to Seek Immediate Dental Care?
Recognizing when to seek urgent dental care is crucial for addressing severe cavity symptoms promptly and preventing complications:
Signs that Indicate Urgent Attention is Needed:
- Severe Pain: Persistent and intense toothache that does not respond to over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Swelling: Swelling of the gums or face, indicating a possible infection or abscess.
- Prolonged Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or pressure that persists beyond normal discomfort.
Steps to Take if Experiencing Severe Symptoms:
- Contact Your Dentist: Immediately call your dentist to explain your symptoms and seek advice.
- Follow Instructions: Follow any instructions given by your dentist in Richmond, such as taking pain relievers or applying cold compresses.
- Emergency Dental Visit: If advised, schedule an emergency dental appointment to receive timely treatment and relief.
Recognizing the signs of a severe cavity is essential for timely intervention and preserving dental health. Early detection through regular dental check-ups and prompt treatment can prevent complications like infections or tooth loss, ensuring a healthy smile for years to come.
